Navigating the Wild World of Laboratory & Imaging Tests for Fertility Patients
While I use my East Asian medical diagnostics with everyone, some patients would be best served by adding additional testing. These tests can range from simple home based information such as basal body temperature and ovulation detector tests. Other patients benefit from blood, salivary and imaging tests. It is within Dr. Rozenn’s scope of practice to offer and interpret functional medicine and conventional testing.
While the time-tested diagnostic tools of East Asian medicine give critical information for fertility treatments, Western laboratory and imaging tests can also guide treatment plans. They provide a waLab tests are a valuable assessment tool. They allow the clinician a behind-the-scenes look at the patient, providing both an initial diagnosis and a benchmark for measuring the success of a treatment plan. In the world of fertility, lab tests are a common language shared by different practitioners. The most important task of the fertility specialist is to assist patients in maximizing their window of opportunity.
The ability to spot red flags in a patient’s work-up will allow the practitioner to effectively guide the patient in considering the most appropriate treatment options in a timely fashion. Red flags include male fertility factor (poor sperm), diminished ovarian reserve (poor egg quantity and quality), blocked fallopian tubes and/or other structural concerns, hormonal imbalances, and any other significant issues that may interfere with one’s fertility.
When to Test
The fertility work-up for men:
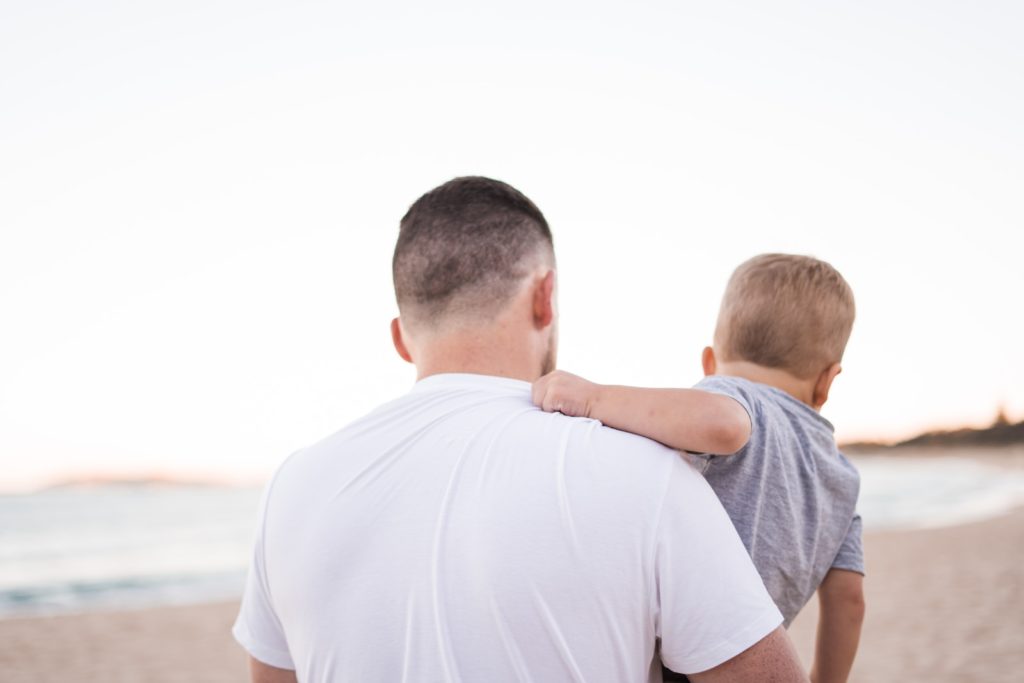

The fertility workup for women is age dependent:
- At 30 years old – completed after one year of trying to conceive
- At 35 years old – completed after 6 months of trying to conceive
- At 40 years old – completed at the beginning of trying to conceive

Testing Methods For Men
Semen Analysis
What we want to know: how many swimmers are there with each ejaculation? This is the total motile sperm, or TMS. Total motile sperm is calculated using the volume, concentration, and motility.
A semen analysis can give us a lot of data such as how many swimmers exist in each ejaculation. It can also give us details on seminal volume, concentration, motility and morphology. It can not tell us if sperm can penetrate an egg or other important details. Sometimes blood work is necessary to uncover important male fertility issues.
Testing Methods For Women
A surge of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) occurs approximately 24 hours before ovulation. With conception, timing is everything. Urine test kits monitor the LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and help predict the time of ovulation, so you can optimize the timing of intercourse to help ensure that sperm will be present when the egg is released.
AMH is a relatively new marker whose role in assessing a woman’s fertility is still being determined. AMH levels reflect the quantity, but not the quality of the follicles. The most established role for AMH measurements is before IVF is initiated, because AMH can be predictive of the ovarian response, or how many eggs are expected to respond to the stimulation medication.
High levels of estradiol at this point in your cycle may signal of poor egg quality or quantity. High levels of estradiol suppress FSH production.
This is the “pro-gestation” hormone, and adequate levels are needed to maintain a healthy pregnancy. Progesterone is only secreted after ovulation, so it can also be used to confirm ovulation. Typically we measure progesterone 7days past ovulation.
Elevated levels of DHEA-S may be found in PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome). DHEA-S is considered an androgen, along with testosterone, and can interfere with normal ovulation. Androgens are known as the “boy” hormones. Women have these hormones, too, just in smaller amounts. When levels become elevated, they can interfere with our “girl” functions.
An ultrasound can look at both the ovaries and the uterus. For the ovaries we are counting the number of the follicles present. When imaging the uterus, we are measuring the thickness of the endometrial lining, and looking any abnormalities such as fibroids, polyps, or a septum.
Questions? Contact Us

